The term “vitamin E” is always associated with the dominant form in the body, alpha-tocopherol. It’s less appreciated that vitamin E comes as a family of eight, and collectively they provide a spectrum of health benefits that are impossible to replicate with alpha-tocopherol alone. [footnote]For reference, there are two families of vitamin e molecules: tocopherol and tocotrienol, and each one has 4 different geometries: alpha, beta, gamma and sigma, making 8 total.[/footnote]
In particular, the tocotrienols are a subclass of vitamin E compounds that are remarkably therapeutic, but have long been considered useless.
Even at the highest peaks of the industry, the acknowledgement of the tocotrienols’ benefits has been exceedingly faint. For example, in the chapter on vitamin E from the textbook I keep at home the authors had this to say about the tocotrienols:
The tocotrienols do not seem to possess any biological significance at this time.
Hmmmm……
How could it be that these disregarded vitamers have an effect on our health?
More Than Just An Antioxidant
Vitamin E gets its status as a vitamin because it’s the body’s primary antioxidant for fats. alpha-tocopherol is the primary form used to this effect, hence the confusion about it being the only legitimate source of vitamin E.
However, if you peep closer into the looking glass it turns out the tocotrienols have a variety of uses within the body that go above and beyond vitamin E’s most common functions.
They are:
- Reduce cholesterol synthesis. In a process distinct from other compounds, the tocotrienols modify the shape of HMG-CoA reductase, which is the rate limiting step in cholesterol synthesis. Its modified shape silences the effect of the enzyme and causes the cell to destroy it. Statins are a class of cholesterol lowering drugs that neuter the same enzyme, but do so by mimicking HMG-CoA R w/in the body and blocking it from its preferred pathway. The fact that the tocotrienols have the same effect as statins but with different methods means they might provide a complimentary treatment for those trying to lower their cholesterol.
- Protects the brain from oxidative damage. Your nervous system is very sensitive to pollutants and the tocotrienols protect the brain from oxidative stress caused by excess glutamate, homocysteine, and prostaglandins, all of which lead to cognitive decline over time.
- Reverses the spread of cancerous cells. For the time being this has only happened in test tubes and not humans, but certain types of tocotrienols activate your cells’ trash compactors that cause tumors to start eating themselves, thus halting irregular cell growth. [footnote]Again, note the importance of this only happening in vitro and not in humans, so the clinical relevance of this is mute. Ie, I’m not saying they cure cancer![/footnote]
It ought to be noted that these benefits are in addition to the typical roles provided by vitamin E within the body. What’s more, the tocotrienols appear to be more potent as an antioxidant than alpha-tocopherol itself!
The trienols have three double bonds in their side chain which makes them less saturated and allows them to more easily embed themselves in the cell membranes of fatty tissues. In organs like the brain and liver alpha-tocotrienol has shown to be more than 40x more effective at reducing free radicals than regular vitamin E.
If the tocotrienols are so great, it begs the question of why they’re given so little attention. Vitamin E was discovered in 1938, so why so little movement on them in the last 78 years?
The biggest reason is that the body doesn’t absorb them particularly well. The good news however, is that it doesn’t need to because the tocotrienols exert their effect at very small concentrations. This is especially true for their ability to protect the brain. Supplementing with 200 mg of tocotrienols will raise your serum levels to 1 uM, which is enough for the tocotrienols to completely demonstrate their neuroprotective effect.
What’s more, it looks like the body has “secret” pathways for transporting only the trienols, particularly to the skin which are especially thirsty for the trienols. So the fact that the body’s primary transport proteins are 8.5X more selective for alpha-tocopherol just isn’t that important for their therapeutic potential.
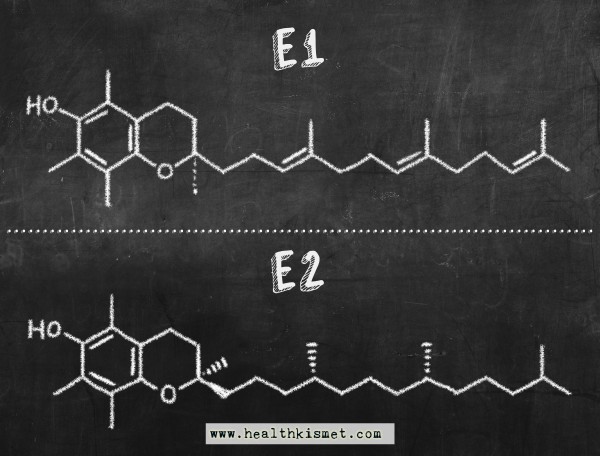
K1, K2…..E1, E2?
Vitamin K has now been subdivided into two subclasses, denoted as K1 and K2. The two compounds have subtly different geometries which changes how they travel throughout your body and get into your tissues. K2 stays in your circulation 6x longer than K1 after you eat it, and this makes enough difference that for a lot of uses K2 is vastly superior to K1 when used deliberately.
It might be time to develop similar nomenclature for vitamin E. The more it’s studied the more it becomes clear that each version of the vitamin has its own unique properties, making it hard to generalize about what exactly vitamin E is good for.
For example, the cholesterol effect is most acute with alpha-tocotrienol, but alpha-tocopherol actually has the opposite effect, making a test with mixed vitamin E self-defeating.
Likewise, the neuroprotection effect is only seen with alpha-tocotrienol, and gamma/sigma tocotrienol are the only versions of the vitamin that inhibit the growth of cancer cells in cell line studies.
So clearly one can easily trip themselves up when talking about vitamin E without making specific note of what type they’re taking.
Gimme Gimme Gimme
Palm oil’s the best natural source of the tocotrienols and full spectrum vitamin E is pretty easy to find in supplementary form if you look for it.
The use of vitamin E to reduce cholesterol in humans is not well validated, but the neuroprotective benefits are. There is a particular blend of tocotrienols called Tocomin Suprabio that’s been put through clinical trials and has shown to be effective.
If you’re looking to source the tocotrienols its best to buy it from a company called ExcelVite, which is the only company that has produced tocotrienols at scale in a facility that’s GMP certified. They make the Suprabio brand of vitamin E but also sell it directly as well.


Thanks for this detailed information, Jonathan. If you use palm oil in cooking, do you think it still gives the same vitamin benefits?
LikeLike
Hey Clarissa……good question!
Vitamin is fairly sensitive to heating and light, so exposing palm oil to temperatures above 50 degrees C will probably result in pretty rapid loss. About 20-30%.
If you don’t like the taste it’d actually be a good idea to rub some on your skin, which is a natural reservoir for vitamin E.
LikeLike
great article as always. does anyone know of a multivitamin that contains the tocotrienols?
LikeLike
Honestly I don’t think there are any. A few like Mercola’s have mixed tocopherols but no tocotrienols. Nutriplex gets their fat soluble vitamins from bovine organs so that might have some tocotrienols but it doesn’t specify anything on the label. I’ve looked for a while and haven’t had any luck.
LikeLike
Agree with prior approval, there are no multivitamins with full spectrum vitamin e inside of it that I know of.
Mixed tocopherols are easier to find.
LikeLike
great post really helping people for vitamin E form…
LikeLike
Great article! I found another great source for vitamins, check this out.
Research Verified Review
LikeLike